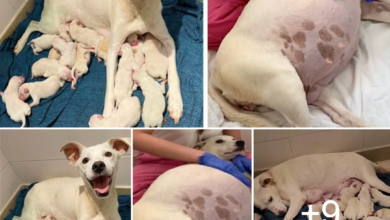
When Can Dogs Get Pregnant?

Are you a dog owner who is curious about when your furry friend can become pregnant? Understanding the reproductive cycle of female dogs and factors that affect canine fertility can help you determine the best time to breed or prevent unwanted pregnancy.
Female dogs typically begin their reproductive cycle between six months to one year of age, depending on their breed and size. This cycle, which lasts about three weeks, includes four stages: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus.
During the fertile stage of estrus, which lasts approximately seven to ten days, female dogs release eggs and are receptive to mating. However, there are several other important considerations when it comes to canine fertility.
The Reproductive Cycle of Female Dogs
Did you know that female dogs go through a reproductive cycle, during which they can become pregnant if they mate with a male dog? This cycle is known as the estrous cycle and it typically lasts for 21 days.
During this time, hormonal changes occur in the female’s body that prepare her for mating and pregnancy. The estrous cycle can be divided into four stages: proestrus, estrus, diestrus, and anestrus.
Proestrus is the first stage and it usually lasts for around nine days. During this time, the female dog experiences vaginal bleeding and swelling of the vulva. She may also display signs of restlessness and increased urination.
Estrus is the second stage of the estrous cycle and it usually lasts for around nine days as well. This is when ovulation occurs and the female dog is most fertile. At this point, she will allow males to mate with her but only if she is receptive to them.
Understanding these different stages of a female dog’s reproductive cycle can help you determine when she may be able to get pregnant based on breeding season or other factors that affect canine fertility.
Factors That Affect Canine Fertility
One major factor that affects a pooch’s ability to reproduce is their age, with younger pups being more fertile than their older counterparts. Canines are generally considered to be at their most fertile between the ages of 2 and 5 years old. After this period, fertility levels can gradually decline until the dog becomes infertile altogether.
Another factor that can impact a dog’s fertility is their overall health. Dogs should receive regular check-ups from a veterinarian to ensure they’re in good reproductive health. It’s also important for potential breeding dogs to undergo canine reproductive health screenings before mating. These screenings can identify any underlying medical conditions that may affect the dog’s ability to conceive or carry a litter to term.
If you’re looking to breed your female dog but she has difficulty conceiving, there are options available such as artificial insemination. This method involves collecting semen from a male dog and directly inserting it into the female’s reproductive tract using specialized equipment. Artificial insemination can increase the chances of conception even when natural mating isn’t possible due to factors such as distance or behavioral issues.
When it comes to breeding dogs, it’s important not only to consider the female’s fertility but also that of the male partner. In the next section, we’ll explore some factors that affect male dog fertility and how they impact breeding success rates.
Male Dog Fertility
If you’re interested in breeding your male dog, it’s important to understand the basics of sperm production. This includes knowing how long it takes for sperm to mature and how many are produced per ejaculation.
Determining your dog’s fertility can involve examining semen quality and conducting a physical evaluation by a veterinarian. By understanding these key points, you can make informed decisions about breeding your male dog and increasing the chances of successful reproduction.
Understanding Sperm Production
As male dogs mature, they begin producing sperm in their testes through a process called spermatogenesis. This involves the production of haploid cells called spermatozoa, which are then stored in the epididymis before being released during ejaculation.
The rate of sperm production varies among different breeds and individual dogs but on average, it takes about 60 to 70 days for sperm to fully develop.
Sperm motility is an important factor for successful fertilization. It refers to the ability of the sperm cells to move actively and swim towards the egg for fertilization. Hormonal regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining this function, as testosterone levels influence both the quantity and quality of sperm produced.
Understanding how these factors affect sperm production can help determine a male dog’s fertility and whether or not he is able to successfully reproduce with a female mate.
How to Determine Fertility
To determine a male dog’s fertility, it’s important to evaluate their sperm quality through a semen analysis. This process involves collecting a sample of the dog’s semen and examining it under a microscope to assess the quantity, motility, and morphology (shape) of the sperm cells. Studies have shown that up to 75% of breeding failures are due to poor sperm quality, so understanding a male dog’s fertility is crucial for successful breeding.
Determining when a female dog is fertile can be more challenging. Unlike humans who have visible ovulation signs such as menstrual bleeding or changes in cervical mucus, dogs do not show obvious physical changes during ovulation. Fertility testing may involve measuring hormone levels or performing vaginal cytology (microscopic examination of vaginal cells) to determine when ovulation occurs.
Once both male and female dogs’ fertility are assessed and confirmed, breeders can proceed with responsible breeding practices.
Breeding Dogs
Breeding dogs can be a fulfilling experience for pet owners who want to expand their furry family. However, before you start breeding your dog, it’s important to consider some health considerations and breeding techniques.
Firstly, it’s essential to make sure that your dog doesn’t have any underlying medical conditions that could affect the pregnancy or the puppies’ health. A veterinarian should conduct a thorough physical examination of the female dog and perform diagnostic tests such as blood tests and ultrasound to ensure she’s healthy.
Secondly, you should carefully choose a mate for your dog based on factors such as breed compatibility, temperament, and health history. It’s also crucial to know when the female dog is fertile because this affects the likelihood of conception. The timing of breeding can be determined by monitoring changes in vaginal discharge or by using an ovulation test kit.
Once you have selected the right mate and determined the ideal time for breeding, it’s time to introduce them. Breeding typically happens naturally without any intervention from humans as long as both dogs are interested in each other. After successful mating, keep an eye on your dog’s behavior and watch out for signs of pregnancy such as appetite changes or lethargy.
Breeding dogs requires careful planning and consideration of various factors such as health considerations and breeding techniques. Once you have successfully bred your dog with a compatible mate during her fertile period, it’s time to wait for signs of pregnancy in dogs which will be discussed in detail in the next section.
Pregnancy in Dogs
Now that you’ve learned about the process of breeding dogs, it’s time to talk about pregnancy in dogs. Dogs can get pregnant starting from six months of age, but it’s not recommended as they’re still growing and developing. The ideal age for breeding a dog is between one to two years old.
Once your dog becomes pregnant, the gestation period lasts for approximately 63 days. During this time, there are several signs that you can look out for to determine if your dog is indeed pregnant. These include a decrease in appetite, lethargy, and nipple enlargement.
It’s important to note that unwanted pregnancies in dogs can easily occur if proper precautions aren’t taken. In the next section, we’ll discuss steps you can take to prevent unwanted pregnancies in your furry friend.
Preventing Unwanted Pregnancy
Just like how we use birth control methods to prevent unwanted pregnancy in humans, there are also options available for our furry companions. It’s important to consider these options as preventing unwanted pregnancies can have a significant impact on your dog’s health and overall quality of life.
Here are some birth control options you may want to consider:
- Spaying: This is the most common method used by pet owners and veterinarians alike. In this procedure, the ovaries and uterus of female dogs are removed, making them unable to reproduce. Aside from preventing unwanted pregnancy, spaying also offers several benefits such as reducing the risk of certain cancers and eliminating heat cycles that can be stressful for both you and your dog.
- Neutering: This method involves removing the testicles of male dogs, which makes them unable to impregnate females. Like spaying, neutering also has numerous health benefits such as decreasing aggression and reducing the risk of prostate cancer.
- Contraceptive injections: These are hormone-based injections that prevent ovulation in female dogs for a certain period of time. While they can be effective in preventing pregnancy, they don’t offer any other health benefits like spaying or neutering.
- Condoms: Yes, condoms for dogs exist! They work similarly to human condoms but are designed specifically for canine anatomy. However, using condoms alone isn’t an ideal solution as they can slip off or break during intercourse.
Ultimately, choosing a birth control option depends on various factors such as your dog’s age, breed, health status, and lifestyle. Consulting with your veterinarian is crucial in helping you make an informed decision on what method best suits your furry companion’s needs.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve made it to the end of this informative article on canine reproduction. By now, you should have a good understanding of the reproductive cycle of female dogs, factors that affect fertility in both male and female dogs, and how to breed dogs properly.
Now that you’re armed with all this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about when and how to breed your dog. But here’s the thing: even though you know all about preventing unwanted pregnancy in dogs, sometimes accidents happen.
So just remember, if your furry friend does end up pregnant unexpectedly, don’t panic – there are plenty of resources available to help you through it.
In conclusion, while we hope that this article has provided valuable information for responsible dog breeding practices and preventing unwanted pregnancies, it’s important to remember that sometimes life doesn’t go according to plan. So stay prepared but also be ready for the unexpected twists and turns that come along with owning a beautiful pup. Good luck!
Read more: